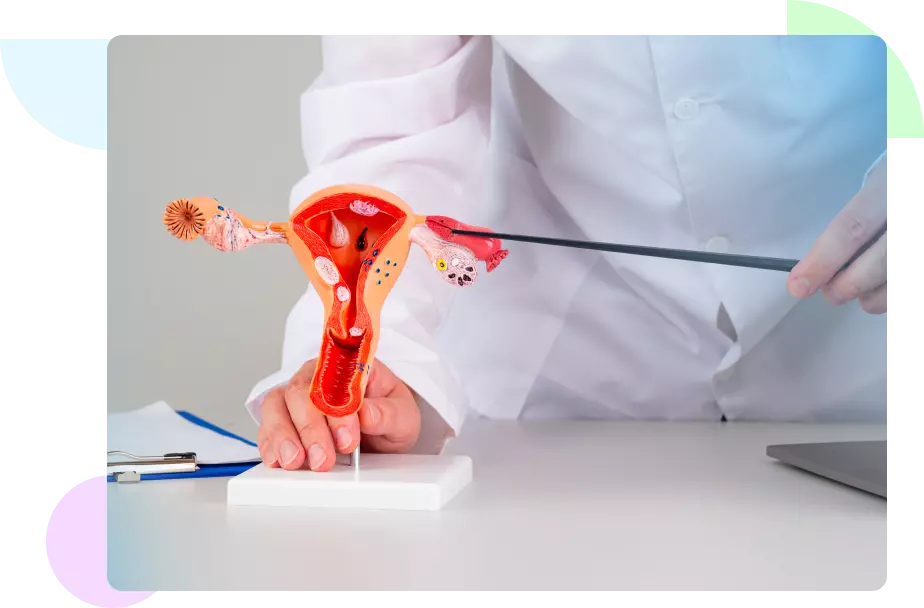
A woman's reproductive system is surgically removed during a unilateral salpingo-oophorectomy, removing one ovary and one fallopian tube. Usually, this treatment is carried out to treat or prevent diseases including endometriosis, ovarian cysts, benign tumors, or ovarian cancer limited to one ovary.
It could also be advised to lower the risk of ovarian cancer in high-risk people or in situations of tubal pregnancy.
When fertility preservation is sought, unilateral salpingo-oophorectomy is regarded as a conservative approach since it preserves the ability of the remaining ovary and fallopian tube to reproduce normally.
Various forms of salphino-oophorectomy exist, depending on the extent of the procedure and the organs removed:
One ovary and fallopian tube are removed during the process. If the opposite ovary and fallopian tube are healthy but there is a disease that affects only one side—such as a cyst or tumor—this may be done.
In this operation, both the ovaries and fallopian tubes are removed. It can be done for some reasons, including managing diseases like severe endometriosis or treating cancer. It can also be done to prevent ovarian cancer in high-risk individuals.
It is the removal of the ovaries and fallopian tubes in their entirety. It's frequently carried out as a prophylactic against ovarian cancer, especially in women who have a significant family history of the condition or who have certain genetic variants
A Unilateral Salpingo-Oophorectomy is a surgical technique in which one ovary and its associated fallopian tube are removed. . A laparoscope, which is a narrow tube with a camera, and specialty surgical equipment are first introduced via tiny incisions created in the belly.
Using a laparoscope, the surgeon may see within the organs and guide surgical instruments to remove the damaged fallopian tube and delicately dissect the ovary.
The surgeon makes sure that the remaining components are intact and that there is no significant bleeding after removing the ovary and fallopian tube. After that, the wounds are sealed with surgical tape or stitches, and a sterile dressing may be used.

For various medical disorders that affect one side of the reproductive system, unilateral salpingo-oophorectomy is done.
Post-operative care is essential to achieving the best possible recovery and reducing the risk of complications following a unilateral salpingo-oophorectomy. To reduce their agony, patients usually take painkillers.
They are also constantly watched for any indications of infection or anesthesia-related side effects. To allow the body to heal, physical activity is initially restricted. Specialized wound care instructions are given to maintain the surgery site clean and encourage healing.
Dietary guidelines emphasize drinking plenty of water and resuming regular meals gradually as tolerated. Follow-up consultations are planned to evaluate the state of recovery, track any symptom changes, and talk about any long-term effects, such as issues with hormone balance or fertility.
