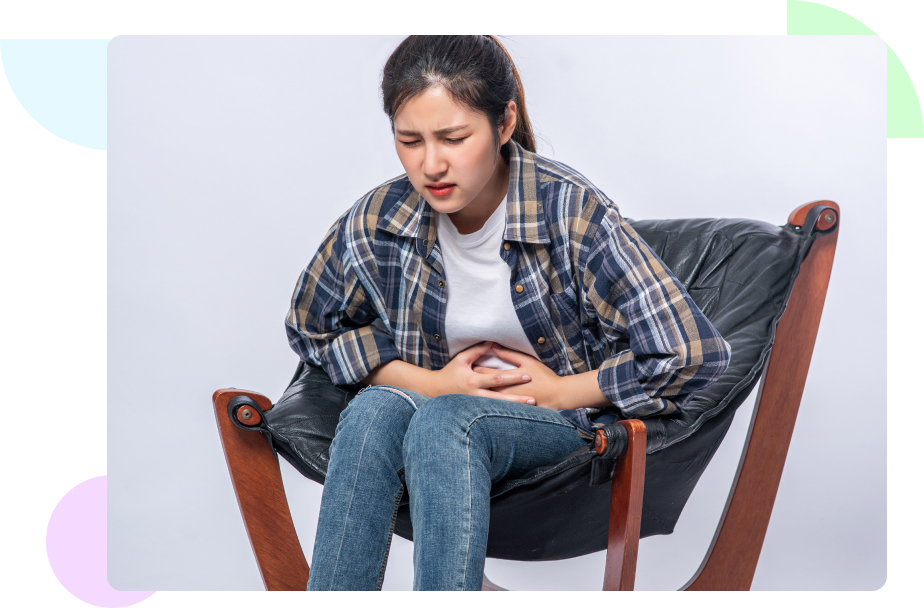
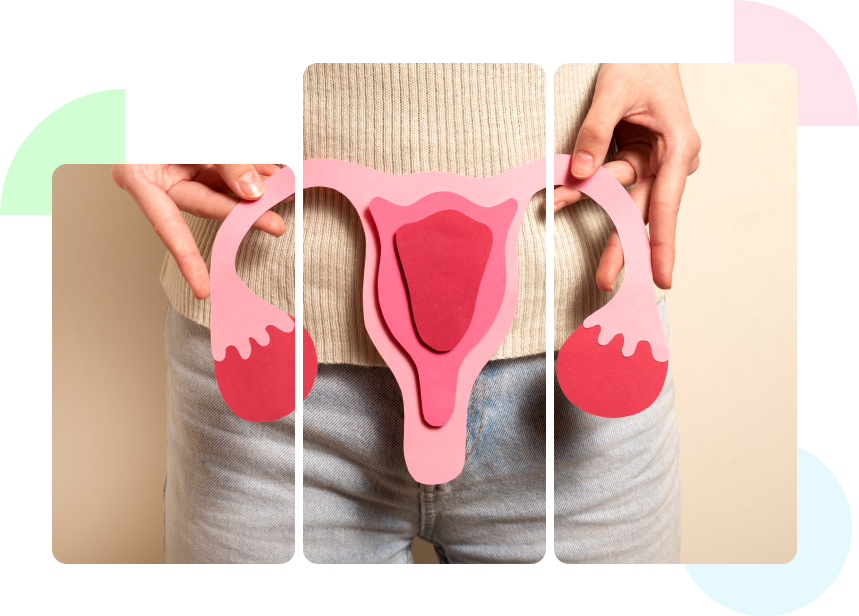
Polycystic Ovary Disease, or PCOD, is a prevalent hormonal condition affecting fertile women. It is typified by an imbalance in reproductive hormones, which causes irregular menstruation periods and the ovaries to form tiny sacs filled with fluid called cysts.
PCOD in women might manifest as irregular or protracted menstrual cycles, hirsutism—excessive facial and body hair growth—acne, and weight gain.
Although the precise origin of PCOD is unknown, a mix of environmental and genetic variables, such as insulin resistance and hormone imbalances, are thought to be involved. Fertility can also be impacted by PCOD, as irregular ovulation can make conception challenging.
PCOD (Polycystic Ovary Disease) symptoms include:

Although the exact causes of PCOD are unknown, a mix of environmental and genetic factors is thought to be the cause of the illness.
Hormonal imbalance is a significant influence, especially when it comes to women's higher-than-average amounts of androgens, or masculine hormones, like testosterone. This hormonal imbalance causes the ovaries to operate abnormally, which results in irregular ovulation and the development of tiny sacs filled with fluid on the ovaries called cysts.
Additionally often linked to PCOD is insulin resistance, a condition in which the body's cells do not respond to insulin as intended. Increased blood insulin levels brought on by insulin resistance have the potential to raise androgen levels and interfere with ovarian function.
Accurate diagnosis is necessary to receive the right care. A medicine expert will frequently do a comprehensive examination as part of the diagnosing procedure. The physician may also suggest further testing to validate the diagnosis.
Key diagnostic tests for PCOD include:
Physical Examination: Evaluate the pelvis for signs like enlarged ovaries, and assess symptoms such as hirsutism and acne.
Bod Tests: Check hormone levels (testosterone, estrogen, LH, FSH) and insulin levels to detect hormonal imbalances and insulin resistance.
Ultrasound: Use transvaginal ultrasound to visualize the ovaries and identify multiple small cysts (follicles) typical of PCOD.
Other tests: It include thyroid function and adrenal function tests to rule out other conditions resembling PCOD.

The goal of PCOD (polycystic ovarian syndrome) treatment is to control symptoms and achieve better hormonal balance, which will improve reproductive and general health. To manage menstrual cycles, lower testosterone levels, and treat conditions like acne and hirsutism, hormonal birth control tablets are frequently administered.
Adopting a nutritious diet low in processed sugars and carbs to control insulin levels, engaging in regular exercise to encourage weight reduction and enhance insulin sensitivity, and practicing stress management to lower cortisol levels are all important lifestyle changes.
It is possible for women who are attempting to conceive to utilize drugs like letrozole or clomiphene to trigger ovulation. Surgical procedures such as ovarian drilling or assisted reproductive technologies (ART) may be explored when medication is not enough.
Maintain a Healthy Weight: Eat a balanced diet low in processed foods, and rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins to control insulin levels and prevent weight gain.
Regular Physical Activity: Engage in regular exercise like running, cycling, or brisk walking to manage weight and improve insulin sensitivity.
Avoid Smoking and Excessive Alcohol: Steer clear of these substances to maintain overall hormonal health.

